Ask the Specialists
Voice Disorders
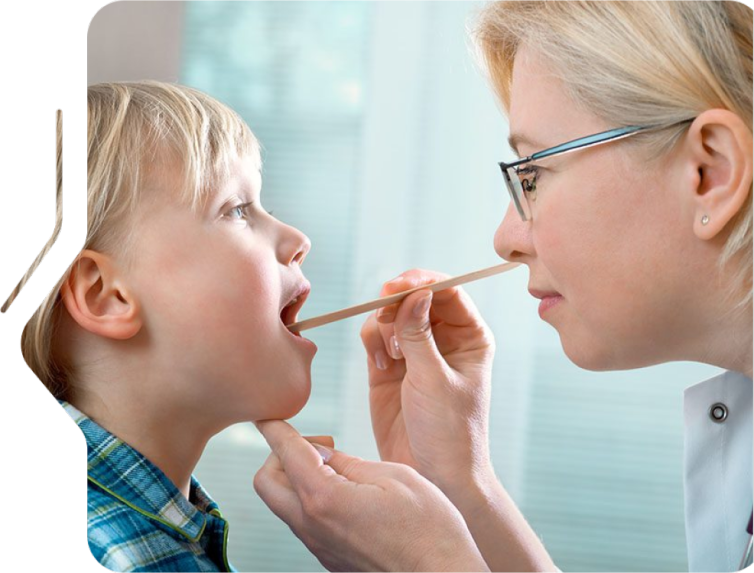

Voice disorders are conditions that affect the quality, pitch, volume, or duration of the voice, often resulting from overuse, injury, allergies, or medical conditions affecting the vocal cords. Common symptoms include hoarseness, loss of voice, and vocal fatigue. Treatment may involve voice therapy or surgical intervention depending on the cause.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of voice disorders typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by an ENT specialist. This may include a thorough medical history, physical examination, and specific tests to assess voice function.
A common procedure used in the diagnosis is a laryngoscopy, which allows the doctor to visualize the vocal cords and identify any abnormalities. Additional tests may include:
- Voice Assessment: An evaluation of voice quality, pitch, and volume.
- Stroboscopy: A specialized technique to observe vocal cord vibration.
- Acoustic Analysis: Computerized analysis of voice parameters.
Treatment options for voice disorders vary depending on the underlying cause and may include:
- Voice Therapy: Guided exercises and techniques to improve voice quality and reduce strain.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics to treat infections.
- Surgery: In cases of structural abnormalities or significant lesions on the vocal cords.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a tailored treatment plan. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in achieving the best outcomes.
Preventive Measures
Preventive Measures for Voice Disorders
- Maintain vocal hygiene
- Use proper vocal technique
- Limit irritants (e.g., smoking, excessive alcohol)
- Rest your voice when needed
- Warm up your voice before extensive use
- Avoid dehydrating substances (e.g., caffeine)
- Manage stress effectively
- Seek professional guidance when necessary
- Educate yourself about vocal health
Common causes include vocal strain, allergies, respiratory infections, and underlying medical conditions like acid reflux.
Symptoms such as persistent hoarseness, breathiness, or voice loss can indicate a voice disorder. Consult a specialist for evaluation.
Treatment options may include voice therapy, medications, or surgical interventions, depending on the diagnosis.
To prevent voice disorders, it is essential to maintain good vocal hygiene, stay hydrated, and avoid straining the voice. If you experience persistent voice changes, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Yes, professions that require frequent speaking or singing, such as teachers, singers, and public speakers, are more prone to voice disorders. Proper vocal techniques can help mitigate risks.